What Is ABS Plastic?
What is ABS plastic? Learn the meaning, properties, advantages, disadvantages, uses, and manufacturing methods of ABS plastic for industrial and commercial applications.
ABS plastic plays a critical role in modern product manufacturing, especially where durability, design flexibility, and cost efficiency must work together. Known chemically as acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, ABS is a widely adopted engineering thermoplastic that combines toughness with reliable mechanical performance, making it suitable for both functional components and visually finished parts.
Manufacturers across industries rely on ABS because it performs consistently in demanding environments while remaining easy to process through methods such as injection molding, CNC machining, and 3D printing. In this article, we’ll clearly explain what ABS plastic material is, define the ABS plastic meaning, and explore key ABS plastic material properties that influence real-world performance. You’ll also learn where ABS works best, where it falls short, how it compares to alternative plastics, and how to decide if ABS is the right choice for your application—whether you’re producing parts for North America, Europe, or Asia’s advanced manufacturing markets.
ABS Plastic
ABS plastic—short for acrylonitrile butadiene styrene plastic—is a widely used ABS thermoplastic valued for its balance of strength, impact resistance, and manufacturability. From automotive interiors and consumer electronics to medical housings and 3D-printed prototypes, ABS is a polymer that supports both high-volume production and rapid product development across global manufacturing markets.
This guide explains the ABS plastic meaning, ABS plastic definition, material properties, advantages and disadvantages, processing methods, applications, comparisons, and practical selection tips—optimized for buyers and decision-makers in the USA, Canada, Germany, and Japan.
ABS Plastic Meaning & Definition
What is ABS plastic material?
ABS plastic is an engineering thermoplastic made by polymerizing three monomers—acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene—each contributing a key performance trait:
Acrylonitrile: chemical resistance and thermal stability
Butadiene: toughness and impact resistance
Styrene: rigidity, surface finish, and ease of processing
Together, they form a versatile ABS polymer that performs reliably in demanding industrial environments.
ABS Plastic Material Properties
ABS Plastic Properties & Characteristics
High impact resistance (excellent toughness)
Good strength and stiffness for structural parts
Chemical resistance to many acids, alkalis, and solvents
Electrical insulation suitable for housings and enclosures
Attractive surface finish with easy post-processing
Processability across molding, machining, and 3D printing
ABS Plastic Mechanical Properties (Typical Ranges)
ABS plastic strength (tensile): ~40–50 MPa
ABS plastic stiffness (flexural modulus): ~2.0–2.5 GPa
ABS impact resistance: high (Izod notched typically 150–300 J/m)
Actual values vary by grade, filler, and processing method.
Advantages of ABS Plastic
Why use ABS plastic? Manufacturers choose ABS for its strong performance-to-cost ratio.
Durability & toughness: Withstands impacts and daily wear
Manufacturing versatility: Ideal for injection molding, CNC machining, and 3D printing
Design freedom: Supports complex geometries and tight details
Surface quality: Paintable, polishable, and colorable
Electrical insulation: Safe for electronics enclosures
These ABS plastic advantages make it a go-to material for both prototypes and end-use parts.
Disadvantages & Limitations of ABS Plastic
Like all materials, ABS has trade-offs:
ABS plastic UV resistance: Poor without additives; prolonged sunlight exposure can cause discoloration and brittleness
ABS heat resistance: Moderate—softens at elevated temperatures
Is ABS plastic flammable? Yes, standard grades are combustible (flame-retardant grades are available)
Dimensional stability: Higher thermal expansion than some engineering plastics
Understanding these ABS plastic disadvantages helps ensure proper material selection.
How Is ABS Plastic Made & Processed?
ABS parts are produced using multiple industrial processes, chosen by volume, tolerance, and geometry.
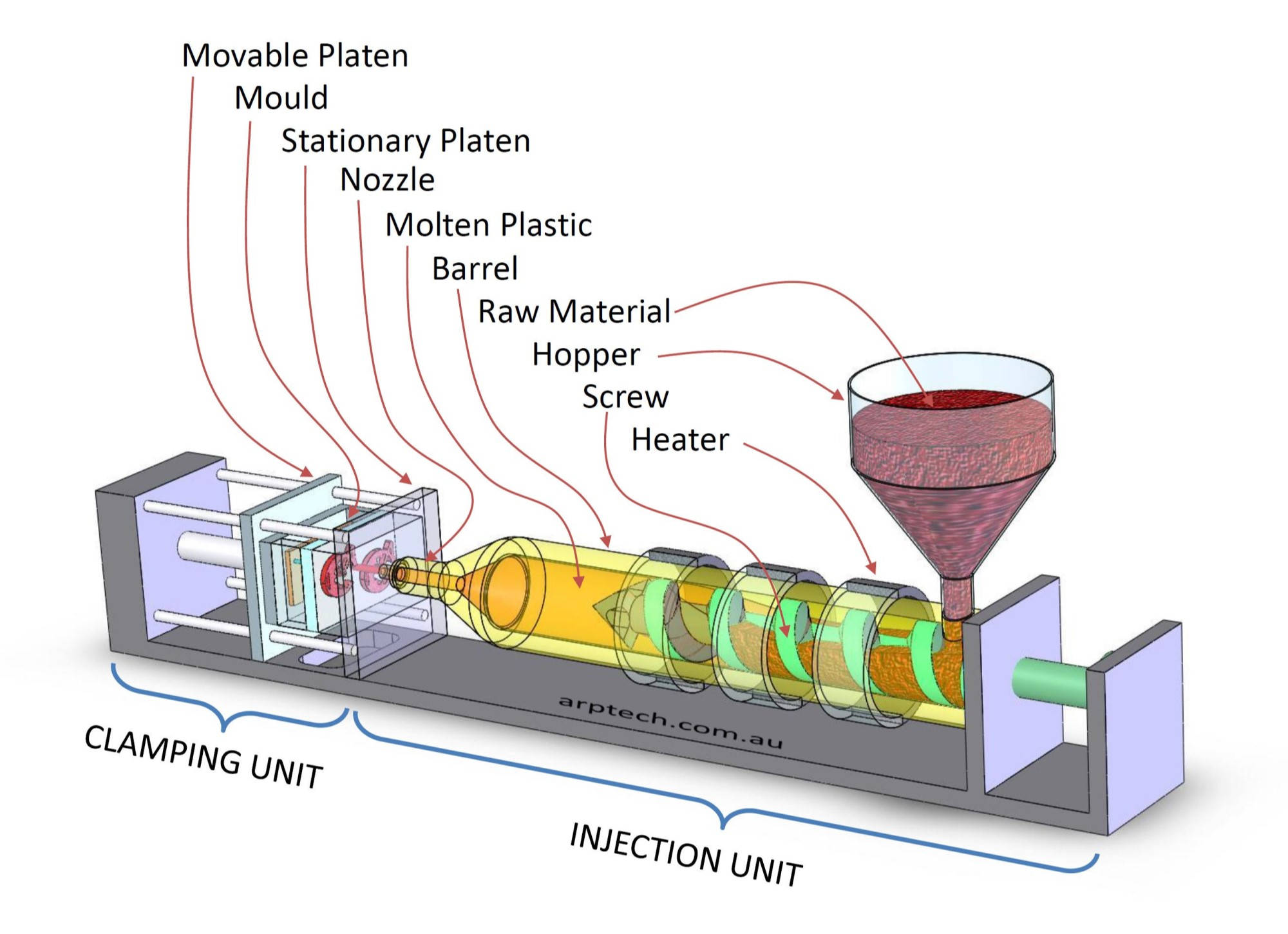
ABS Injection Molding
The most common method for high-volume, tight-tolerance production of complex ABS plastic products.
ABS CNC Machining
Ideal for low-volume, custom, or precision ABS components with fast turnaround.
ABS Plastic 3D Printing
ABS FDM printing: Popular for functional prototypes and jigs
ABS SLA materials / ABS-like resin: Higher detail and surface quality
ABS Extrusion
Used for continuous profiles such as sheets, rods, and tubes.
ABS Thermoforming
Cost-effective for large, thin-wall parts like panels and housings.
ABS Blow Molding
Used for hollow ABS components and containers.
Technical & Performance Data
ABS melting point: ~200–240 °C (392–464 °F)
ABS glass transition temperature: ~105 °C (221 °F)
ABS operating temperature: typically −20 °C to 80 °C
ABS thermal expansion: higher than PC or nylon
ABS fire resistance: standard grades are combustible; FR grades available
ABS Plastic Applications & Uses
Common ABS Plastic Uses
Consumer electronics: keyboards, mice, remote controls, housings
Automotive parts: dashboards, trims, grilles, mirror housings
Medical devices: equipment housings and non-implantable components
Toys & games: durable, safe, moldable products
Appliances: vacuum cleaners, coffee makers, kitchen tools
Sports equipment: helmets, protective gear, enclosures
These ABS plastic applications benefit from the material’s toughness, finish, and manufacturability.
ABS Plastic vs Other Materials (Alternatives)
Plastics Similar to ABS
ABS vs Polycarbonate (PC): PC offers higher heat and impact resistance, but costs more
ABS vs Polypropylene (PP): PP has better chemical resistance and flexibility; ABS is stiffer and tougher
ABS vs Polystyrene (PS): PS is cheaper but far less impact-resistant
ABS vs Polyethylene (PE): PE excels in chemical resistance; ABS offers better rigidity and finish
ABS vs Nylon (PA): Nylon is stronger and more heat-resistant, but more expensive and moisture-sensitive
Choosing among ABS plastic alternatives depends on performance, cost, and environment.
ABS for 3D Printing & Prototyping
ABS 3D printing material is favored for functional prototypes
ABS filament properties include strength and post-processing flexibility
ABS vs PLA: ABS is tougher and more heat-resistant; PLA is easier to print
ABS-like resin enables high-detail SLA prototypes
ABS remains a strong choice for ABS for prototyping when durability matters.
Cost, Safety & Sustainability Considerations
ABS plastic cost: Mid-range; generally lower than PC and nylon
Is ABS plastic safe? Yes, for industrial and consumer products; medical and food contact require compliant grades
Is ABS plastic food safe? Only with certified, food-grade formulations
Is ABS plastic recyclable? Yes—commonly recycled as resin code #7
ABS plastic environmental impact: Recyclability helps, but bio-based alternatives are emerging
When to Use ABS Plastic
Choose ABS when you need:
High impact resistance and toughness
Good surface finish for visible parts
Multiple manufacturing options
Reliable performance at moderate temperatures
FAQ: ABS Plastic
What is ABS plastic used for?
ABS is used in automotive parts, consumer electronics, medical housings, appliances, toys, and 3D-printed prototypes.
Is ABS plastic strong?
Yes. ABS plastic strength and toughness make it suitable for impact-resistant structural components.
Is ABS plastic heat-resistant?
Moderately. It performs well up to ~80 °C; higher temperatures require alternatives like PC or nylon.
Is ABS plastic flammable?
Standard grades are combustible, but flame-retardant ABS is available.
Is ABS plastic recyclable?
Yes, ABS is recyclable and commonly reprocessed in industrial recycling streams.
ABS vs PLA—what’s better?
ABS is tougher and more heat-resistant; PLA is easier to print and more biodegradable.
Conclusion
ABS plastic is a proven, versatile engineering material that balances performance, cost, and manufacturability. Understanding its properties, limitations, and processing options allows manufacturers and product teams to confidently specify ABS for automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer applications worldwide. When selected correctly, ABS delivers durable, attractive, and cost-effective parts at scale.